Polyclonal Antibody to Beta actin
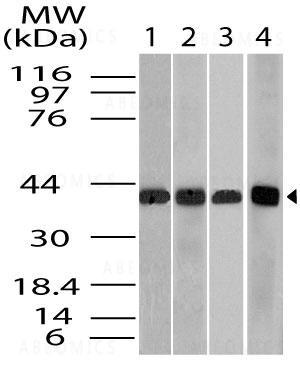
Figure-1: Western blot analysis of Beta actin. Anti- Beta actin antibody (11-13012) was used at 4 µg/ml on 1) Raw, 2) 3T3, 3) Hela and 4) U87 lysates.
Roll over image to zoom in
Shipping Info:
Order now and get it on Tuesday March 03, 2026
Same day delivery FREE on San Diego area orders placed by 1.00 PM
| Format : | Purified |
| Amount : | 100 µg |
| Isotype : | Rabbit IgG |
| Purification : | Protein A Chromatography |
| Content : | 25 µg in 50 µl/100 µg in 200 µl PBS containing 0.05% BSA and 0.05% sodium azide. Sodium azide is highly toxic. |
| Storage condition : | Store the antibody at 4°C, stable for 6 months. For long-term storage, store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze and thaw cycles. |
B-actin (ACTB) has traditionally been regarded as an endogenous housekeeping gene and has been widely used as a reference gene/protein in quantifying expression levels in tumors. It supports fundamental cellular processes in healthy and diseased cells including cell adhesion, migration, cytokinesis and maintenance of cell polarity. However, B-actin is closely associated with a variety of cancers and accumulating evidence indicates that B-actin is de-regulated in liver, melanoma, renal, colorectal, gastric, pancreatic, esophageal, lung, breast, prostate, ovarian cancers, leukemia and lymphoma. This protein is generally found to be up-regulated in the majority of tumor cells and tissues.
Western blot analysis: 4-6 µg/ml:
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic/therapeutics procedures.
1. Panda PK, Naik PP, Meher BR, Das DN, Mukhopadhyay S, Praharaj PP, Maiti TK, Bhutia SK. PUMA dependent mitophagy by Abrus agglutinin contributes to apoptosis through ceramide generation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018 Mar;1865(3):480-495. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 8. PubMed PMID: 2922947
2. Nayak TK, Mamidi P, Kumar A, Singh LP, Sahoo SS, Chattopadhyay S, Chattopadhyay S. Regulation of Viral Replication, Apoptosis and Pro-Inflammatory Responses by 17-AAG during Chikungunya Virus Infection in Macrophages. Viruses. 2017 Jan 6;9(1). pii: E3. doi: 10.3390/v9010003. PubMed PMID: 28067803; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5294972.
3. Panigrahi B, Singh RK, Mishra S, Mandal D. Cyclic peptide-based nanostructures as efficient siRNA carriers. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018 Oct 12:1-11. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1511574. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 30311806.
4. Panigrahi B, Mishra S, Singh RK, Siddiqui N, Bal R, Mandal D. Peptide generated anisotropic gold nanoparticles as efficient siRNA vectors. Int J Pharm. 2019 May 30;563:198-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 Apr 3. PubMed PMID: 30953762.
5. Yavvari PS, Verma P, Mustfa SA, Pal S, Kumar S, Awasthi AK, Ahuja V, Srikanth CV, Srivastava A, Bajaj A. A nanogel based oral gene delivery system targeting SUMOylation machinery to combat gut inflammation. Nanoscale. 2019 Mar 14;11(11):4970-4986. doi: 10.1039/c8nr09599j. PubMed PMID: 30839018.
6. Shahror RA, Linares G, Wang Y, Hsueh SC, Wu CC, Chuang DM, Chiang YH, Chen KY. Transplantation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing FGF21 Facilitates Cognitive Recovery and Enhances Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2019 Jul 12. doi: 10.1089/neu.2019.6422. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 31298621.
| Subcellular location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Post transnational modification: | (Microbial infection) Monomeric actin is cross-linked by V.cholerae toxins RtxA and VgrG1 in case of infection: bacterial toxins mediate the cross-link between Lys-50 of one monomer and Glu-270 of another actin monomer, resulting in formation of highly toxic actin oligomers that cause cell rounding (PubMed:19015515). The toxin can be highly efficient at very low concentrations by acting on formin homology family proteins: toxic actin oligomers bind with high affinity to formins and adversely affect both nucleation and elongation abilities of formins, causing their potent inhibition in both profilin-dependent and independent manners (PubMed:26228148). |
| BioGrid: | 106575. 336 interactions. |
|
There are currently no product reviews
|













.png)













